In our progressively connected world, digital trust and digital security are bo....
Health and Safety in the Workplace

According to International Labour Organization, every year around 2.3 million people globally lose their lives due to work-related accidents or even diseases. This means over 6,000 lives per day are lost in workplace unfortunate events.
All these tragic events have made occupational health and safety management become one of the top concerns for workplaces. All organizations, regardless of how many employees they have or what sector they operate in, should place health and safety plans on their top priorities.
What is a health and safety plan?
A health and safety plan is an organization’s documented plan that addresses workplace hazards and establishes safety measures and procedures. It provides detailed instructions and strategies on how to manage different aspects of health and safety.
What are the most common hazards and risks in a workplace?
Workplace hazards refer to any situation or source that has the potential to cause injuries, damage, or harm to a person in a workplace. Most common workplace hazards can fall into these six core types:
- Biological hazards
- Chemical hazards
- Physical hazards
- Safety hazards
- Ergonomic hazards
- Psychosocial hazards
Biological hazards – It is common for biological hazards to appear in a workplace so it is important to be prepared for them as they can have consequences. Biological hazards are harmful substances produced by organisms.
Some of the most typical biological hazards include:
- Bacteria and viruses
- Mold and fungi
- Harmful plants
- Stinging insects
- Contaminated waste
- Animal droppings
Chemical hazards – Refers to any chemical substances that can cause a health hazard. Based on the type of harm they cause, chemical hazards are categorized as:
- Corrosives
- Irritants
- Teratogens
- Sensitizers
- Mutagens
- Carcinogens
Common workplace chemical hazards can include:
- Acids
- Caustic substances
- Cleaning products
- Heavy metals
- Pesticides
Physical hazards – These are environmental factors that can harm employees. For example:
- Radiation
- Extreme weather
- Extreme noise
- Height
- Pressure
- Machinery and tools hazards
- Electricity
Safety hazards – These are all hazards that make workplace conditions unsafe. Sometimes, safety hazards overlap with physical hazards. Some examples of safety hazards are:
- Exposed wires
- Slippery, falling, or tripping hazards
- Machinery malfunctions
Ergonomic hazards – These are physical workplace conditions that can cause injury to the musculoskeletal system. For example:
- Poor posture
- Heavy lifting
- Improper workstation
Psychosocial hazards – These are work-related factors that can increase stress and can lead to psychological or physical harm. For example:
- High or low job demands
- Poor support
- Poor management
- Low recognition and reward
- Low role clarity
- Poor relationships
- Workplace harassment
- Traumatic events
Plan-do-check-act approach
Plan-do-check-act (PDCA) is a management approach used to continually control and improve processes. This continual improvement cycle is easier to follow, and is effective strategy in managing health and safety processes.
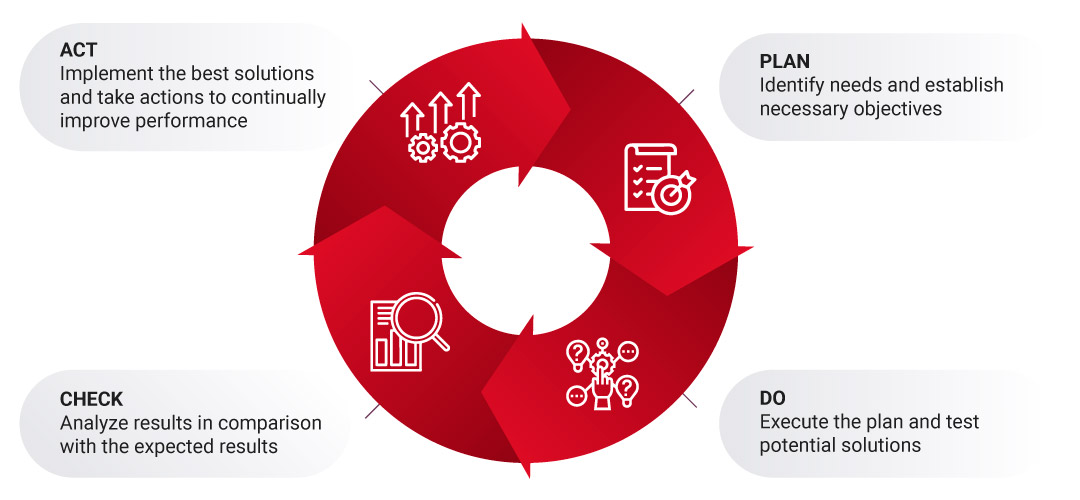
Plan
The planning phase is the first step of the PDCA cycle. During this phase, board members establish a health and safety policy and define the goals and expectations of the organization. The board should be aware of risks and they should plan how to assess and understand the main issues they are facing. This process should be evolving over time in order to address and meet its needs constantly.
Overall, during this stage, the working team will study the concerns, establish objectives and priorities, design and define roles and responsibilities, and determine how the process effectiveness will be evaluated.
Do
After the planning, the doing stage is when the action happens. The main part of the do stage is to identify the risks and find a solution to minimize or eliminate them. As planned ahead, the biggest risks should be prioritized and started with first.
Check
During this phase, performance is monitored, controlled, and assessed by using different methods defined during the planning phase. During this phase, the organization observes, collects, and analyzes data, gathers employee feedback, and also records and reports outcomes.
Moreover, they conduct regular or scheduled inspections, check the operation of workplace precautions, monitor the environment, and carry out health surveillance.
Act
This is the phase when professionals review what has been done so far and how has it been going. If there have been any issues, then the board should revisit the planning stage and then update it.
Overall, health and safety programs focus on some main elements, such as leadership and employee involvement, worksite analysis, hazard identification, assessment, prevention and control, education and training of staff, and program evaluation.
ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety Management System
ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety Management System is the world’s first international standard for Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S). It is applicable to all organizations and it can be integrated with other management systems.
This standard promotes continuous improvement of OH&S performance and it serves as a framework for safety increase, workplace risk minimization, and enhancement of health and wellbeing. This standard will help management develop and implement effective policies and establish proper objectives.
These are some of the main benefits of ISO 45001:
- Reduction and prevention of workplace incident
- Increase employee trust, and reduction of staff turnover or absenteeism
- Enhanced reputation
- Ability to comply with legal and regulatory requirements
- Reduced insurance premiums and claims
Mental health in the workplace
Psychological well-being is considered to be significantly affecting the overall well-being of employees, as well as their job performance. On the other hand, just like mental health impacts the work, the work impacts it as well. As bad as it was, COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of psychological factors, raising awareness which represents a new era for mental health at work.
In accordance, ISO has developed ISO 45003:2021 which is the first global standard offering guidelines on psychological health and safety in workplace management. This standard helps organizations manage psychosocial risks and it promotes the psychological health of workers. ISO 45003 is based on ISO 45001 and is intended to be used together with it.
About the author
Vlerë Hyseni is the Digital Content Officer at PECB. She is in charge of doing research, creating, and developing digital content for a variety of industries. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact her: content@pecb.com


